Blog
Keliods
Keloid is an excessive skin growth that happens when the skin heals excessively or over reacts with no obvious provocation or injury.
It is common among black people which is a risk factor for keloid and can run in families.
A person skin type can predispose the person to having this skin disorder which can manifest following an insult to the skin.
Common causes of keloid include earlobe piercing, burn injury, acne , or after a healed skin injury etc.
However, keloid are not cancers and does not transform to cancer.
But can be itchy, painful or even have ulcers if left untreated.
Keloid tend to increase in size and can become discomforting if left untreated .
Treatment incudes doing nothing for milder forms of keloid and those which do not affect cosmesis, laser therapy, surgery in combination to other modalities, and the use of steroids etc.
For more information about keloid treatment, visit us at Fullhouse Specialist Hospital.
DIABETES A LEADING CAUSE OF AMPUTATION INCIDENCE IN OUR COMMUNITIES.
Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism in which the body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar level) causing blood sugar level to be abnormally high.
There are three most common classification of Diabetes which include type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (insulin dependent or juvenile diabetes), type 2 Diabetes Mellitus(adult onset diabetes Mellitus), and Gestational Diabetes (Diabetes in pregnancy).

Health burden
Diabetes Mellitus is a growing global health emergency and one of the most challenging health problems of the 21st century. In 2019, it was estimated that about 463million people had diabetes globally. In sub-Saharan Africa, 15.5 million people were estimated to be living with DM in 2001.(Science direct, primary care diabetes, June 2022)
Risk Factors
Some risk factors associated with Diabetes mellitus include;
. Positive family history of Diabetes
. Age > 35 years
. Overweight and obesity
. Presence of hypertension
. Sedentary lifestyle or physical inactivity
. Diabetes in pregnancy, etc.
Warning Signs and Pattern of Presentation of Diabetes Mellitus
Unlike most Tropical infections like Malaria, Typhoid fever, etc., Diabetes Mellitus type 2, more specifically, which accounts for 85-95% of all Diabetes, in its early stage may be unnoticed by the individual being affected as it’s been reported to have a latent asymptomatic period of subclinical stages which often remains undiagnosed for several years. Hence, many individuals with type 2 Diabetes, in its early stage, may not know however, that they have this disease.
Warning Signs
The usual pattern of presentation include symptoms which is noticed at its earlier stage and can be seen as it’s Warning Signs. this include;
- Frequent urination (polyuria); also occuring at night (nocturia) (about 2 to 3 times in a 6 to 8 hour of night rest)
- Dry mouth and Excessive thirst (feeling of thirst more commonly, which results in wanting to drink water a lot) (polydypsia)
- Increased hunger (feeling of extreme, insatiable hunger) (polyphagia)
- Weight loss
- Frequent infection of mouth, skin, urinary tract, etc.
2. Complications of Diabetes mellitus
Awareness and timely intervention of these Warning Signs and symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus is crucial in its timely management which would likely delay or curb some of its complications which forms a huge health burden. Some of these complications are;
Kidney disease such as Chronic Kidney disease;
Hypertension, heart attack, stroke;
Eye sight problems, (Retinopathy) which could lead to a vision loss etc.
3. Amputation from Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic foot Disease
Amputation is a serious and disabling complication of Diabetes mellitus which results from Diabetic foot disease.
Diabetic foot
Excess and uncontrolled blood sugar damages the nerves on the extremities of the body, more commonly on the foot (sensory neuropathy) leading to reduced feeling in the feet. more so, Diabetes mellitus leads to narrowing of small blood vessels that supplies the foot, a condition known as Peripheral artery disease. Hence, in an uncontrolled Diabetic condition state with a reduced feeling of the foot , foot injury becomes more common, and in a state of injury to the foot with a poor blood supply, the injuries becomes less likely to heal easily, leading to long lasting injuries and chronic leg ulcers which in a state of infection could affect the bones and, subsequently, with delayed and failed intervention could lead to the death of the foot, necessitating Amputation.
Diabetic foot and lower extremity amputation are the most prevalent and feared complication of Diabetes mellitus. A report by CDC (centre for disease control and prevention ) revealed about 15 – 40 times higher burden of amputation among Diabetic patients than non Diabetic patients.
4. Timely intervention
An important factor in the prevention of complications associated with diabetes millitus is Timely intervention. This is an important remedy in Diabetes management which is both crucial in preventing its complication and having a better health outcome.
This includes
- Early Detection (Screening)
- Management (intervention)
Screening
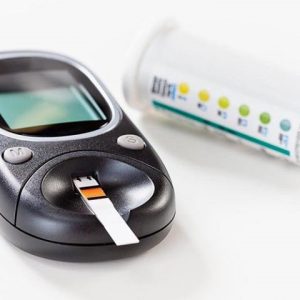
Diabetes mellitus and more commonly Type 2 Diabetes is a common and serious illness in our communities and globally. However , it is thought that a good number of those with this illness are unaware that they have this serous illness. Because more often than not, the symptoms of Diabetes and Diabetes mellitus type 2 are not obvious, early screening may help people avoid the more serious complications of this disease, of which Amputation from Diabetic foot disease is a major one.
Who Should Be Screened for Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends screening for diabetes in adults aged 45 years or older and screening in persons with multiple risk factors regardless of age.
The recommended interval for the screening of asymptomatic patients is three years. This interval can be short in patients who have obesity and other major risk factors for developing diabetes.
The recommendations for those with a high risk of developing diabetes are candidates for more early/frequent screening, early behaviour intervention, and intensive treatment.
What Test Is Used to Screen for Diabetes?
The fasting plasma glucose test (FPG) or the haemoglobin A1C test can be used for screening.
Negative
If the screening test for diabetes is negative, continue to have follow-up screening tests as routinely as possible or as recommended by your physician. However, your doctor may do further screening tests for diabetes if they suspect that you have diabetes or prediabetes and your initial screening result is negative.
In addition, the chances of getting diabetes can be lowered by reducing excess weight, keeping the blood pressure and lipids at normal levels, and regular exercise .
Positive
If the screening test for diabetes is positive, the individual may need further testing to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Thereafter, Medications, along with a diet, regular exercise regimen, and lifestyle program, to help in the management of blood sugar level and prevention of serious complications would be recommended .
Management
The goals in caring for patients with diabetes mellitus are to eliminate symptoms and to prevent, or at least slow, the development of complications. Microvascular (i.e., eye and kidney disease) risk reduction is accomplished through control of glycaemia and blood pressure;
Macrovascular (i.e., coronary, cerebrovascular, peripheral vascular) risk reduction, through control of lipids and hypertension, smoking cessation, and aspirin therapy; and
Metabolic and neurologic risk reduction, through control of glycaemia.
Overall, this could be achieved through
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels,
- dietary management,
- maintenance of physical activity,
- keeping of weight and stress under control,
- oral medications and, if required, insulin use via injections or pump.
5.Summary
Diabetes Mellitus is an illness with a rising global health burden and Amputation through Diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot disease is preventable. Early detection and intervention is crucial in the timely intervention as well as in the prevention of the complications associated with this illness which are detrimental to health.
